Research
By developing computational tools, the OMNI Lab aims to address key needs in modern medicine: (i) automated analysis relieves the requirement for highly-skilled radiologists; (ii) discovery of novel markers for diagnostic screening; (iii) software for portable devices, thus broadening access to high-quality care in the developing world; and (iv) investing in sophisticated software while leveraging existing imaging hardware provides a large cost benefit to an already constrained healthcare system. To achieve these goals, our research focuses on the following topics:
- Characterizing the Fetal Brain
- 2D-3D US Reconstruction
- Clinical Translation
- Deep Learning Methodology
Characterising the Fetal Brain
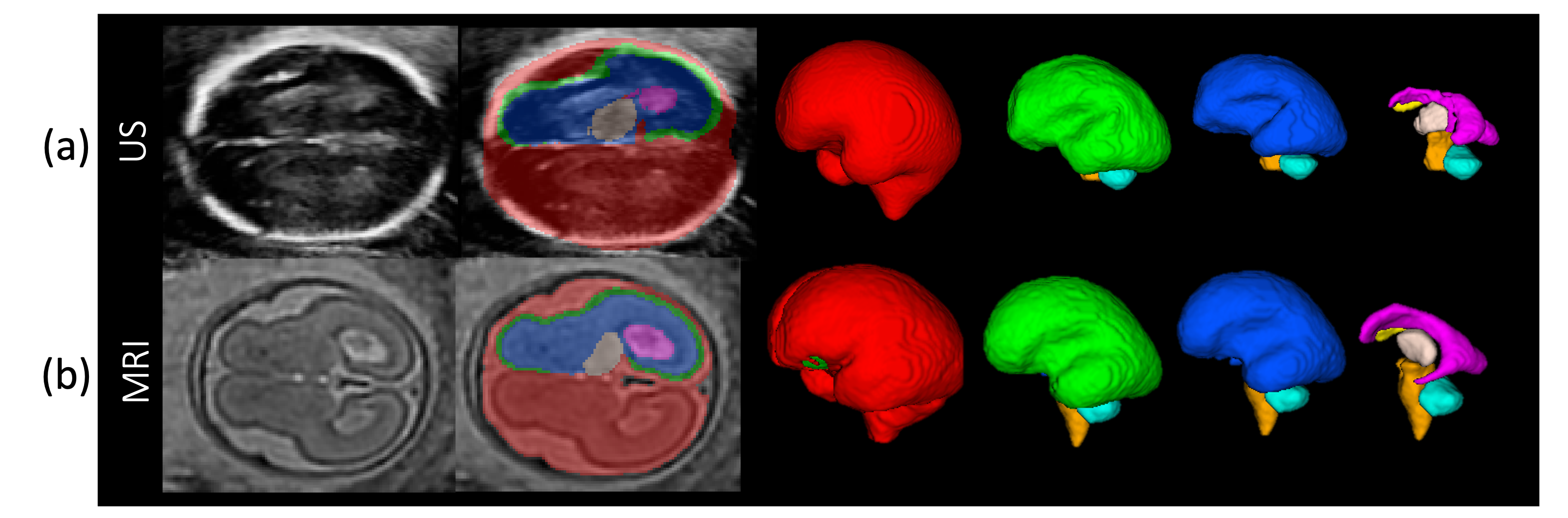
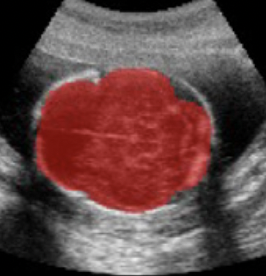
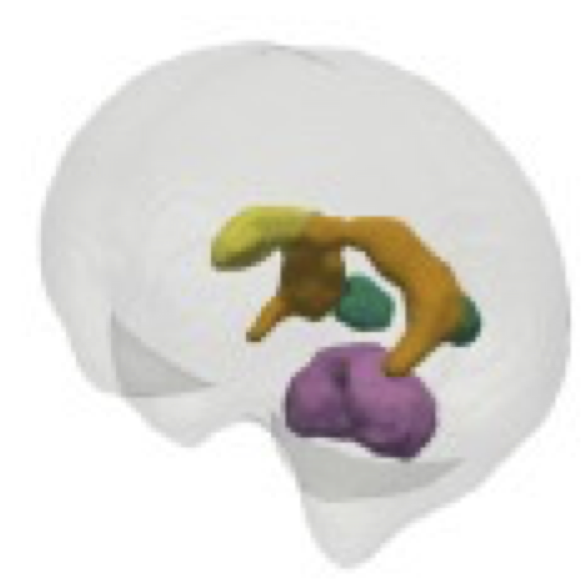
Normal development of the human brain can be characterized by precisely timed growth and folding of its surface (cortex), with deviations often associated with poor cognitive outcomes. Advances in ultrasound (US) imaging technology now make it possible to visualize the cortex and screen for brain abnormalities before birth, from as early as 14 gestational weeks (GW). Working closely with the INTERGROWTH-21st Consortium and healthcare professionals, we develop a range of computational tools for assessing fetal health from US images.
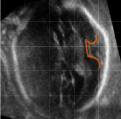
2D to 3D Reconstruction
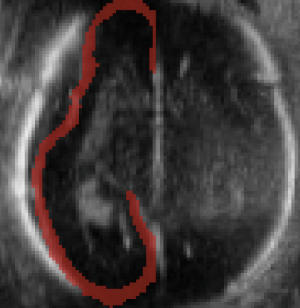
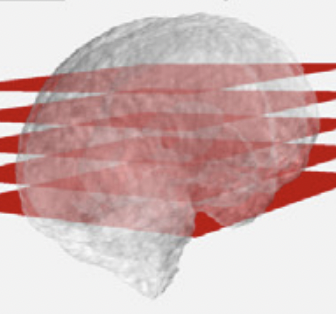
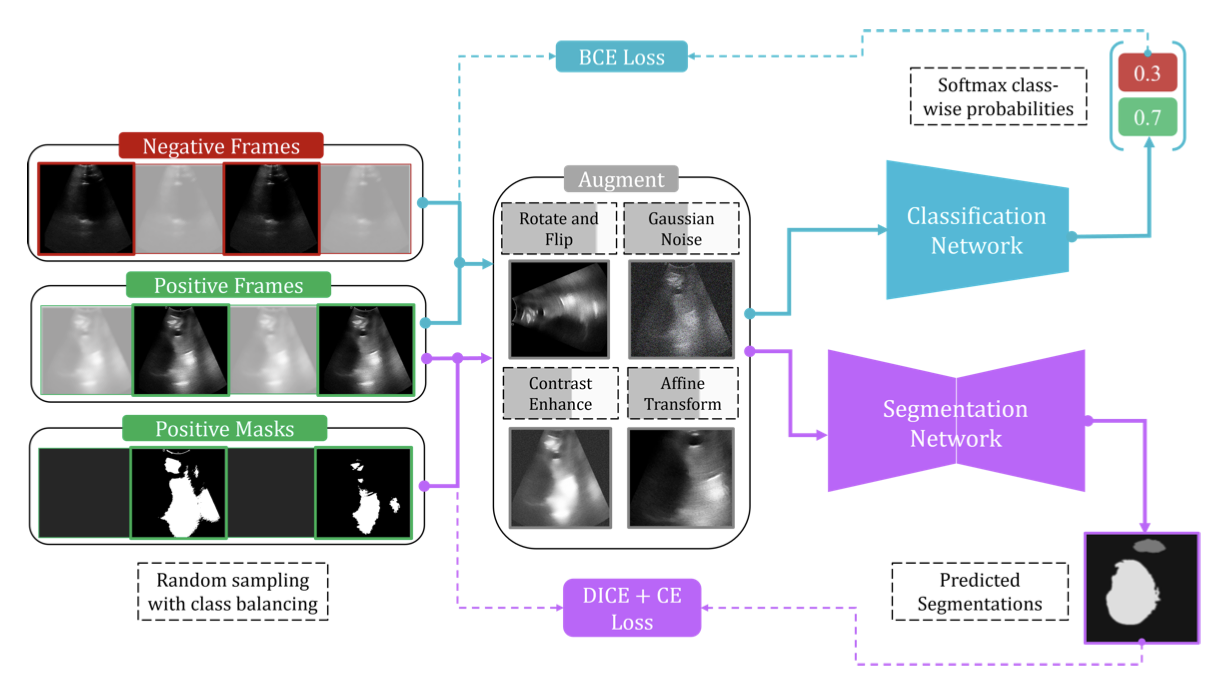
In neuroimaging research, 3D image data is the mainstay for representing anatomical details. However, in conventional clinical practice, pre- and post-natal assessments are performed with 2D video or static US images. The sonographers need to interpret the relationships between the 2D views and 3D brain anatomy and mentally reconstruct a 3D image given just the 2D information. Our goal is to develop methods to reconstruct a 3D brain scan from 2D freehand video acquisitions. We foresee that this would have applications in perinatal clinics, and in LMICs.
Clinical Translation
Deep learning has shown great promise in the research domain, but significant barriers still exist which limit the clinical translatability of deep learning models. Our research aims to tackle these barriers focusing on the challenges of: distributed data and data privacy, model compression, and the development of clinically meaningful biomarkers.
Distributed Data and Data Privacy
Model Compression
Biomarker Development
Deep Learning Methodology
Fundamental to our research is the development of state-of-the-art DL methodology. Key topics include segmentation, interpretability and domain adaptation.